main resource: https://www.amazon.com/Digital-Design-Computer-Architecture-ARM/dp/0128000562
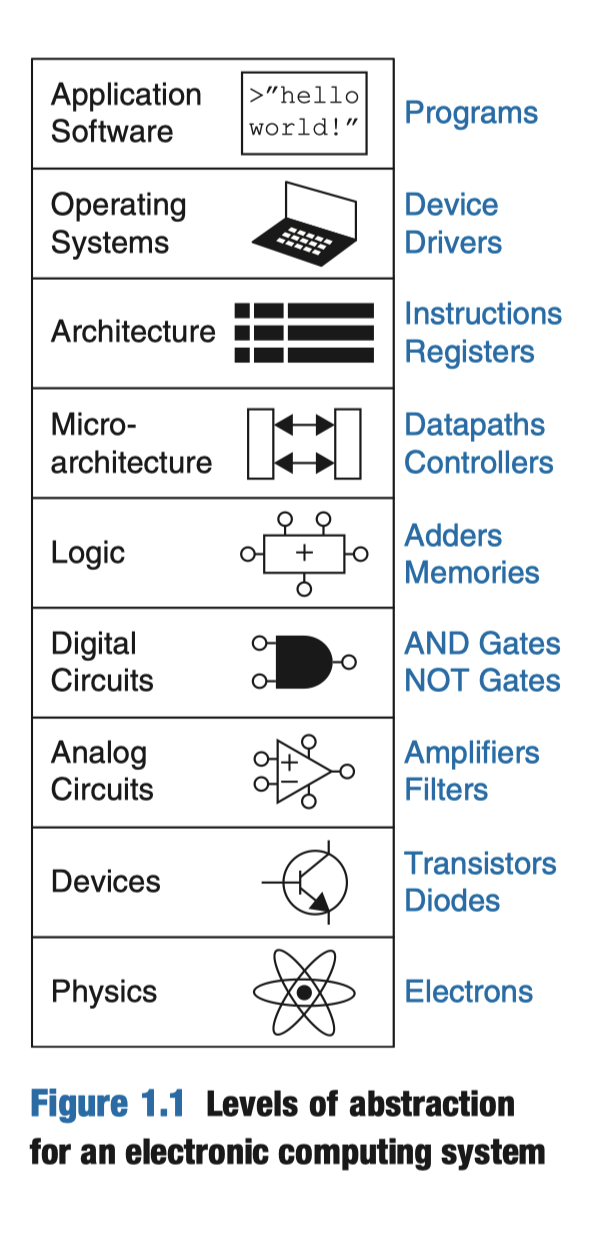
Chapter 1
Analog circuits - Used to make amplifiers; can input and output a continuous range of voltages
Digital circuits - restrict voltages to discrete ranges, which we will use to indicate 0 and 1.
Microarchitecture - links the logic and architecture levels of abstraction.
architecture - abstraction describe a computer from the programmaer’s perspective.
The digital abstraction
The amoutn of information D in a discrete valued variable with N distinct states is measured in units of bits as bits
Bit is short for binary digit.
Continuuous singla theoretical contain infinite amount of infomraiton. Inm pracitce, measurement error limit the information to only 10 to 16 bits for mosot cononitnuoos singals.
George Boole developed system of logic operating on systems known as boolean logic.
Bytes, nibbles, and all that jazz
A group of eight bits is called a byte. It represents one of 2 8 = 256 possibilities. The size of objects stored in computer memories is customarily measured in bytes rather than bits.
A group of four bits, or half a byte, is called a nibble. It represents one of 2 4 = 16 possibilities. One hexadecimal digit stores one nibble and two hexadecimal digits store one full byte. Nibbles are no longer a commonly used unit, but the term is cute.
Microprocessors handle data in chunks called words. The size of a word depends on the architecture of the microprocessor. When this chapter was written in 2015, most computers had 64-bit processors, indicating that they operate on 64-bit words. At the time, older computers handling 32-bit words were also widely available. Simpler microprocessors, especially those used in gadgets such as toasters, use 8- or 16-bit words.
Microprocessor is a processor built on a single chip.
Logic gates
Buffer - From the logical point of view, a buffer is no different from a wire, so it might seem useless. However, from the analog point of view, the buffer might have desirable characteristics such as the ability to deliver large amounts of current to a motor or the ability to quickly send its output to many gates. This is an example of why we need to consider multiple levels of abstraction to fully understand a system; the digital abstraction hides the real purpose of a buffer.
Beneath the digital abstraction
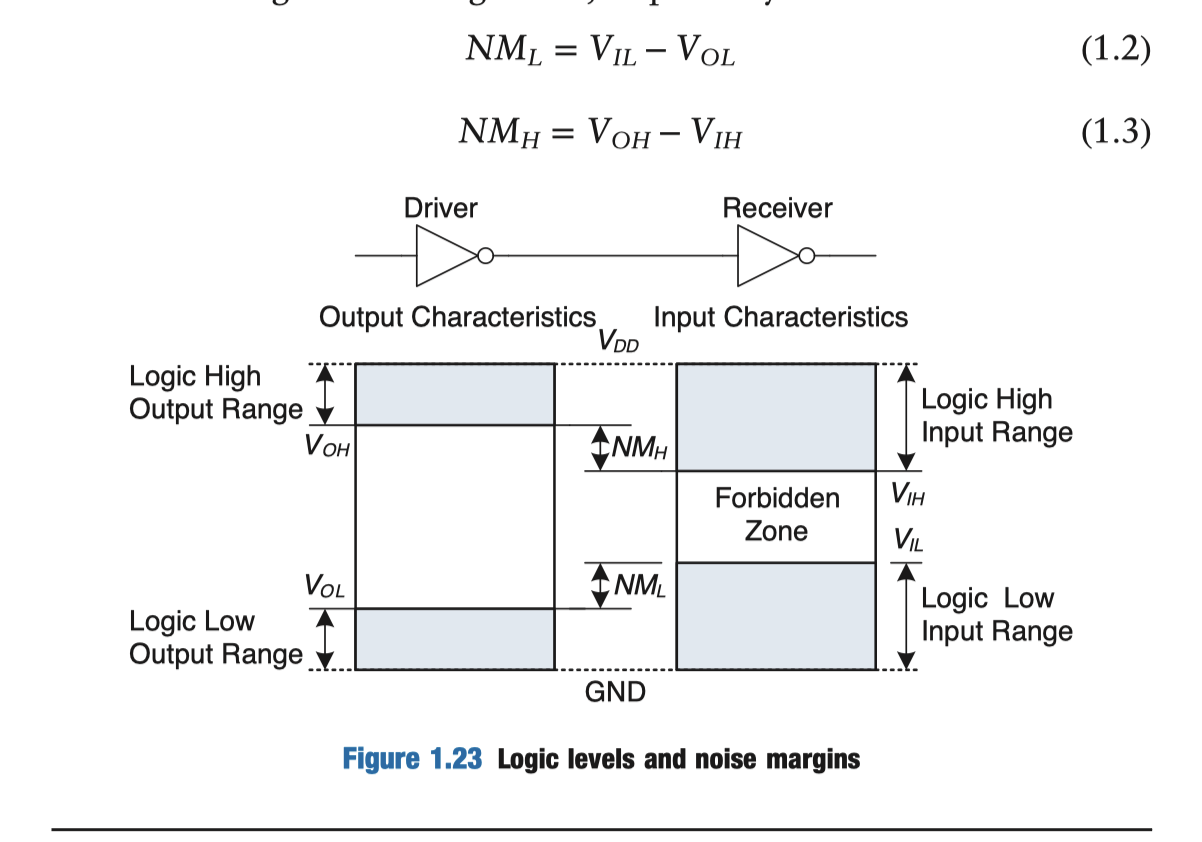
⇒ output low ⇒ input low ⇒ output high ⇒ input high
⇒ highest voltage in the system croms from the power supply and is usually called V_DD In 1970’s and 1980’s technology, V DD was generally 5 V. As chips have progressed to smaller transistors, V DD has dropped to 3.3 V, 2.5 V, 1.8 V, 1.5 V, 1.2 V, or even lower to save power and avoid overloading the transistors.
stands for the voltage on the drain of a metal-oxidesemiconductor transistor, used to build most modern chips. The power supply voltage is also sometimes called , standing for the voltage on the collector of a bipolar junction transistor used to build chips in an older technology. Ground is sometimes called because it is the voltage on the source of a metal-oxidesemiconductor transistor.
DC Transfer Characteristics
DC indicates behavior when an input voltage is held constant or changes slowly enough for the rest of the system to keep up. The term’s historical root comes from direct current, a method of transmitting power across a line with a constant voltage. In contrast, the transient response of a circuit is the behavior when an input voltage changes rapidly.
An ideal inverter
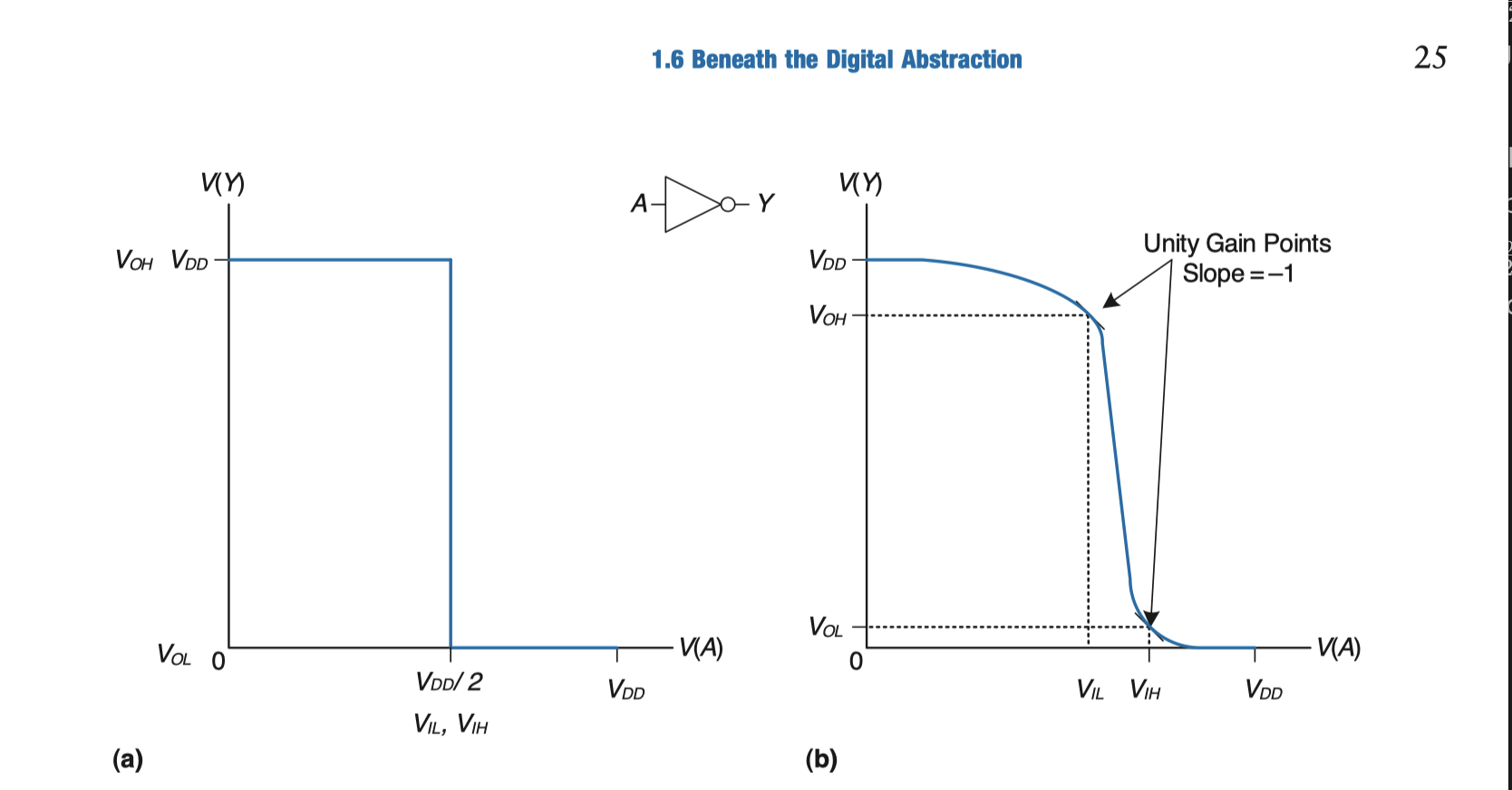 a ⇒ ideal inverter
b ⇒ more realistic inverter
a ⇒ ideal inverter
b ⇒ more realistic inverter
A reasonable place to choose the logic levels is where the slope of the transfer characteristic dV(Y) / dV(A) is −1. These two points are called the unity gain points. Choosing logic levels at the unity gain points usually maximizes the noise margins. If V IL were reduced, V OH would only increase by a small amount. But if V IL were increased, V OH would drop precipitously.
Static discipline
To avoid inputs falling into the forbidden zone, digital logic gates are designed to conform to the static discipline. The static discipline requires that, given logically valid inputs, every circuit element will produce logically valid outputs.
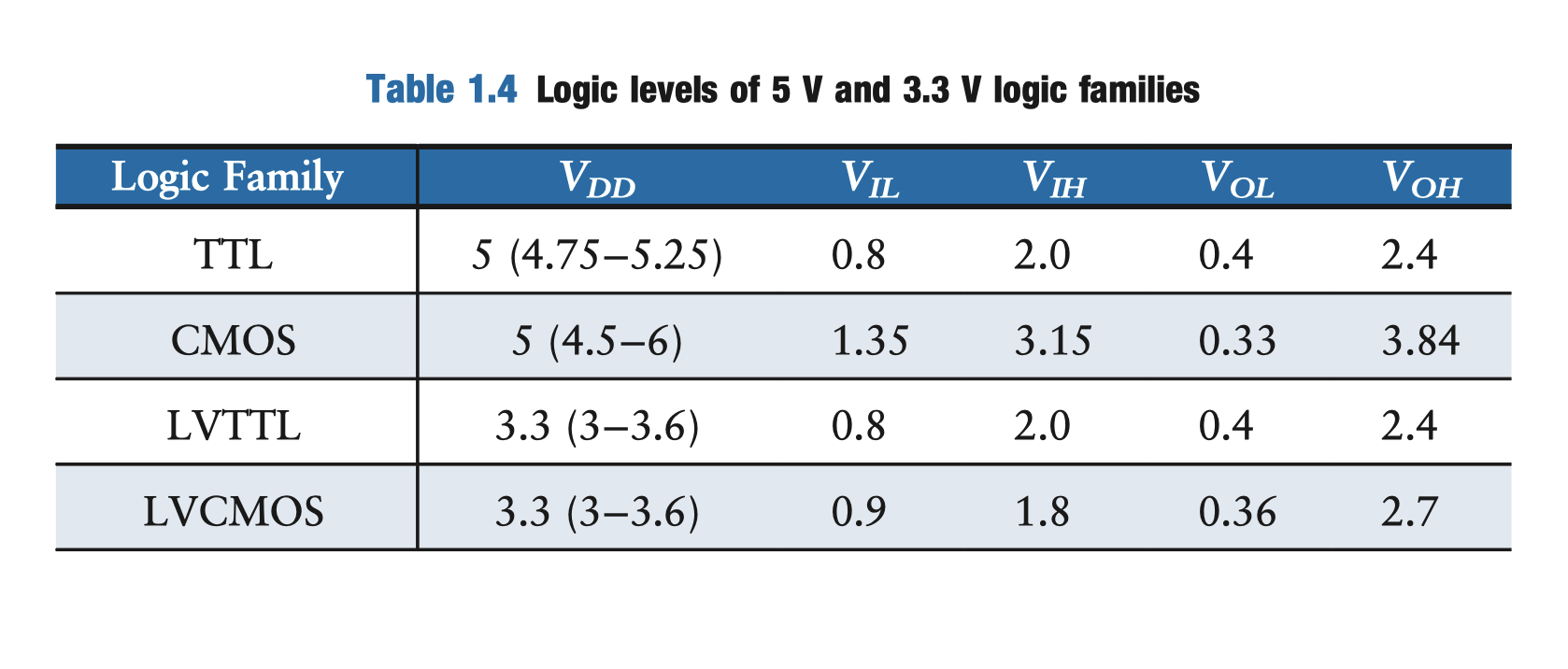
Four major logic families that predominated from the 1970’s through the 1990’s are Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL), Complementary MetalOxide-Semiconductor Logic (CMOS, pronounced sea-moss), Low Voltage TTL Logic (LVTTL), and Low Voltage CMOS Logic (LVCMOS).
Robert Noyce, 1927–1990. Born in Burlington, Iowa. Received a B. A. in physics from Grinnell College and a Ph.D. in physics from MIT. Nicknamed “Mayor of Silicon Valley” for his profound influence on the industry.
Cofounded Fairchild Semiconductor in 1957 and Intel in 1968. Coinvented the integrated circuit. Many engineers from his teams went on to found other seminal semiconductor companies
CMOS Transistors
Transistors: electrically controlled switches that turn ON or OFF when a voltage or current is applied to a control terminal.
Two main types:
- bipolar junction transistors
- meta-oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs or MOS transistors)
Semiconductors
- Made from silicon (group IV atom)
- by itself is a bad conduct
- When you add small amounts of impurities, dopant atoms it becomes a better conductor
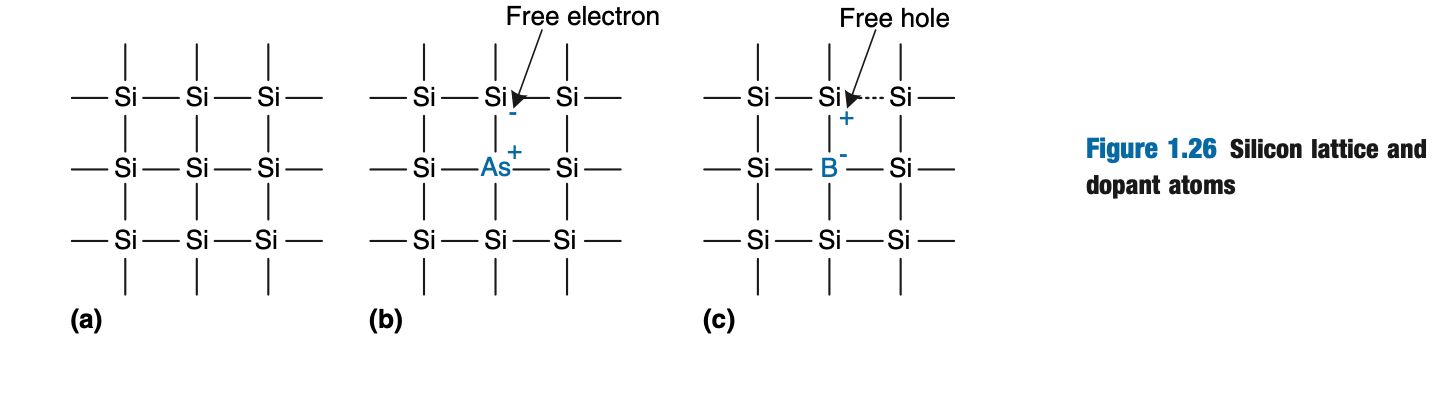
The hole is a lack of nega- tive charge, so it acts like a positively charged particle. Hence, we call boron a p-type dopant. Because the conductivity of silicon changes over many orders of magnitude depending on the concentration of dopants, sili- con is called a semiconductor.
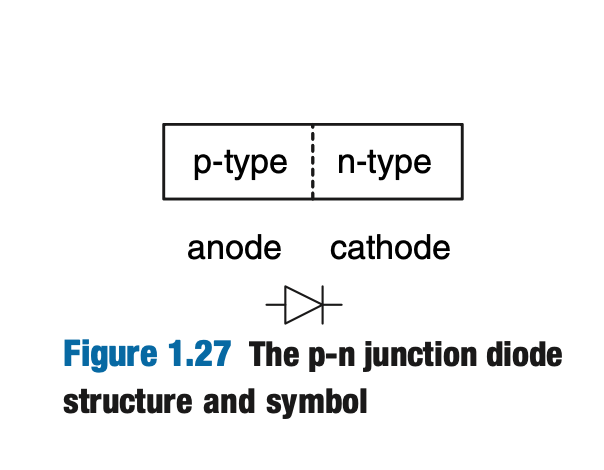
Diodes
The junction between p-type and n-type silicon is called a diode. The p-type region is called the anode and the n-type region is called the cathode
Power Consumption
Combinational Logic Design
Combinational Building blocks
Timing
Prpogation and Contamination Delay